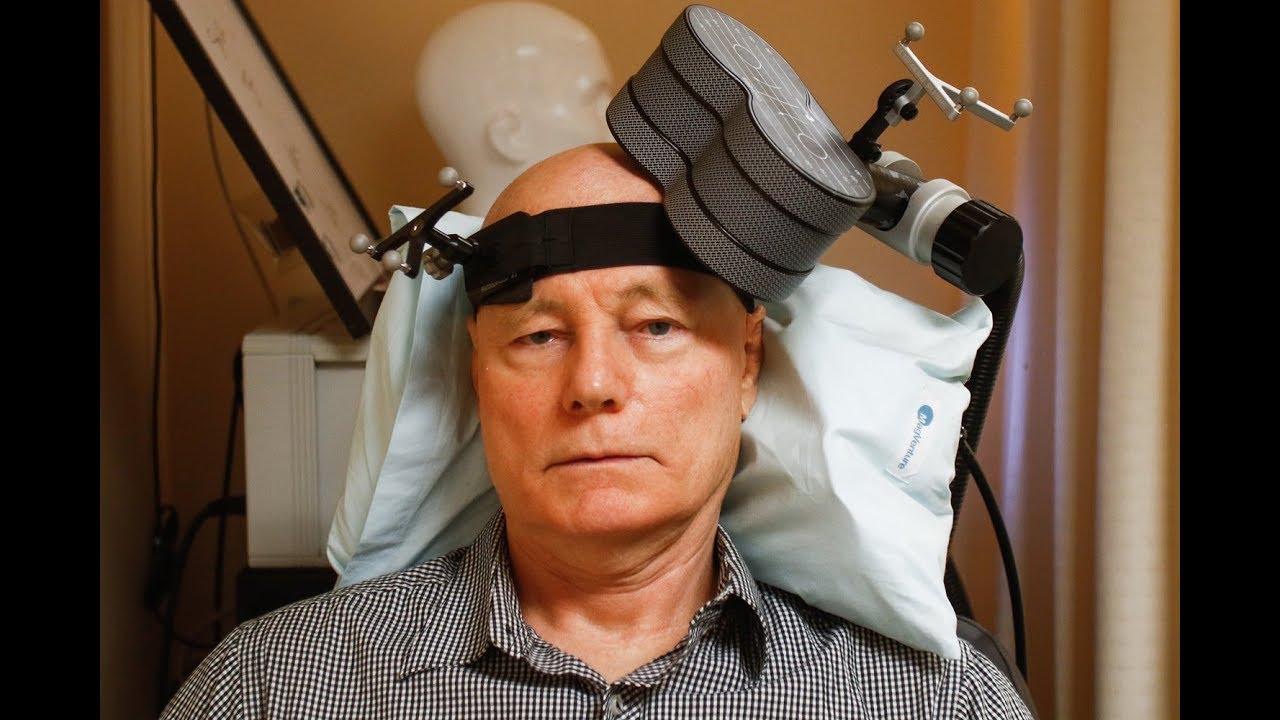
New Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Accelerated Neuromodulation Therapy is a unique form of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation TMS that is intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS). It is a noninvasive brain stimulation treatment that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment-resistant depression in September 2022.
The “accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy” of the Stanford University School of Medicine (“Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Neuromodulation Therapy” – SAINT) is a therapeutic alternative to antidepressants and psychological therapy that has been recently developed for those cases of depression persistent , having given positive results in more than 80% of the study participants, although it should be noted that the sample was small, so it is necessary to know the results by performing it with a larger sample to see if it is a reliable therapy.
This therapy arose from the current situation in which there has been a considerable increase in cases of depression, which is why new treatments are needed to combat depression that are fast-acting and that also offer a high degree of efficacy, while also being safe and tolerable for patients
How is it used?
Accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy is delivered through intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS), which is a type of non-invasive brain stimulation treatment for the treatment of persistent depression that has resisted other treatments such as psychotherapy and antidepressants.
This therapy suggests that the intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) protocol has been improved by following the following premises:
- Perform several sessions a day, with an optimal interval between sessions and for several days in a row.
- Apply a general pulse stimulation dose that is higher than usual (1,800 instead of 600).
- Focus precisely on the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the anterior cingulate cortex.
For its application, 50 sessions of 10 minutes are administered for 5 consecutive days (10 sessions/day) at 90% of the motor threshold at rest, receiving 1,800 pulses per session, with a 50-minute break between sessions. Prior to its application, Stanford researchers preliminarily evaluated the tolerability, feasibility, and efficacy of accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy so that patients are safe and do not suffer any adverse effects when receiving treatment.
Conclusions
Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Accelerated Neuromodulation Therapy is advanced unique form of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation TMS. The results of this innovative therapy for depression that have been very positive. However, it has been carried out with a very small sample, so there is still a long way to go and it has to be approved by the different drug federations and agencies in order to be administered more widely in hospitals around the world.
However, in this small sample, fewer side effects have been seen than in a treatment that has been approved by the US drug regulatory body (FDA), which is “transcranial magnetic stimulation” that is applied daily for a period of 6 weeks and offers a success rate of approximately 50%, so it would be interesting to see more studies on accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy to see if it is a better alternative than transcranial magnetic stimulation.